Orbital Floor Fracture
Low confidence
High confidence
- Age: 23
- Sex: Female
- Modality: CT
- Region: Brain
- Country: N/A
- State: N/A
- City: N/A
- Diagnosis: Blowout fracture of orbit
🧠 AI Suggestion
1) Findings:
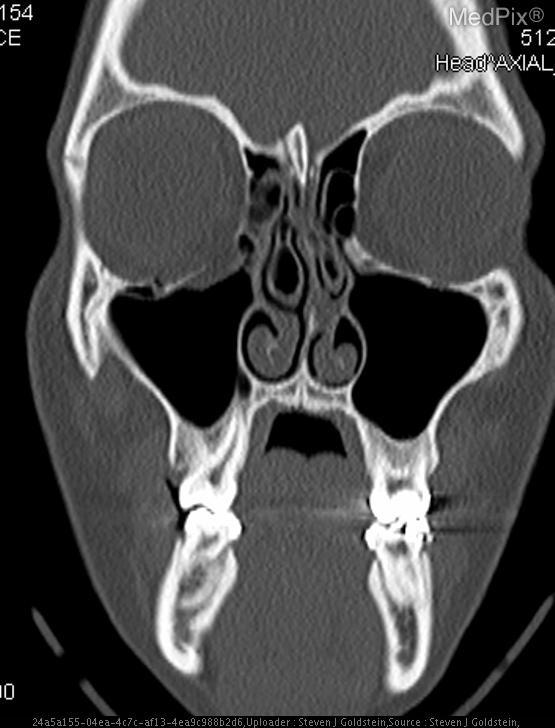
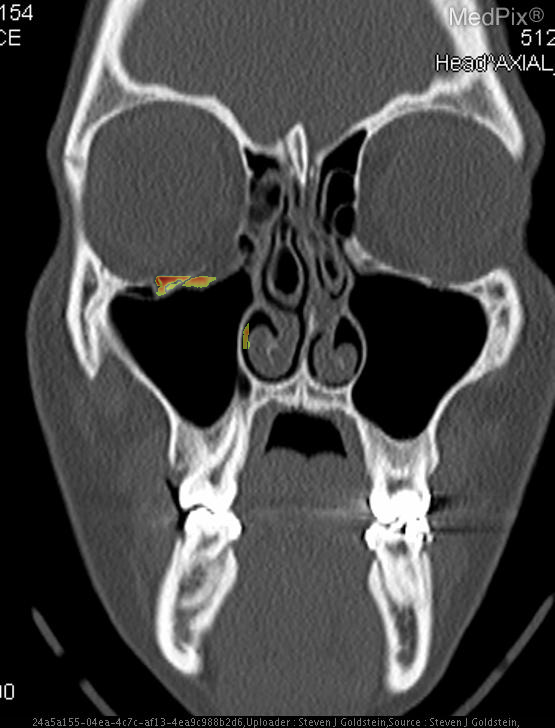
- Coronal CT image shows discontinuity of the orbital floor on the image-left (patient-right) side.
- Herniation of orbital fat and partial inferior displacement of soft tissue into the maxillary sinus on the image-left (patient-right).
- Air-fluid level within the right maxillary sinus (image-left side), consistent with hemorrhage or fluid collection.
- Intact orbital floor on the image-right (patient-left) side.
- Globes are intact bilaterally, without evidence of rupture or significant intraorbital hematoma.
- Nasal septum roughly midline; ethmoid air cells and remaining paranasal sinuses are clear.
- No intracranial abnormalities visible at this coronal slice level.
2) Most likely diagnosis and why:
Orbital floor (blowout) fracture on the image-left (patient-right) side. The CT demonstrates a defect in the orbital floor with herniation of orbital contents into the maxillary sinus, a classic feature of a blowout fracture. The presence of sinus fluid and continuity of orbital fat confirms disruption of the orbital floor. Context consistency: Consistent. Context title and imaging findings are in agreement for an orbital floor fracture. Confidence: 95%.
3) Next best diagnostic step:
A full maxillofacial CT series with thin coronal and sagittal reconstructions should be obtained to assess the exact extent of fracture, possible muscle entrapment, and involvement of adjacent bony structures. Clinical correlation for diplopia, enophthalmos, or limitation of gaze is critical for management planning.
4) Key differential or confirmatory test:
Forced-duction testing can help confirm extraocular muscle entrapment. If visual disturbance or globe injury is suspected, ophthalmologic evaluation with slit-lamp and fundoscopic examination is necessary. MRI orbit can aid in evaluating soft-tissue entrapment if CT findings are equivocal.
5) Possible treatment or management:
** Mild, non-displaced fractures without muscle entrapment may be managed conservatively with oral antibiotics, avoidance of nose blowing, and close ophthalmologic follow-up. Surgical repair (via transconjunctival or subciliary approach) is indicated if there is persistent diplopia, muscle entrapment, enophthalmos >2 mm, or large defect on CT. Early reconstruction helps restore orbital volume and prevent long-term cosmetic deformity.
- Coronal CT image shows discontinuity of the orbital floor on the image-left (patient-right) side.
- Herniation of orbital fat and partial inferior displacement of soft tissue into the maxillary sinus on the image-left (patient-right).
- Air-fluid level within the right maxillary sinus (image-left side), consistent with hemorrhage or fluid collection.
- Intact orbital floor on the image-right (patient-left) side.
- Globes are intact bilaterally, without evidence of rupture or significant intraorbital hematoma.
- Nasal septum roughly midline; ethmoid air cells and remaining paranasal sinuses are clear.
- No intracranial abnormalities visible at this coronal slice level.
2) Most likely diagnosis and why:
Orbital floor (blowout) fracture on the image-left (patient-right) side. The CT demonstrates a defect in the orbital floor with herniation of orbital contents into the maxillary sinus, a classic feature of a blowout fracture. The presence of sinus fluid and continuity of orbital fat confirms disruption of the orbital floor. Context consistency: Consistent. Context title and imaging findings are in agreement for an orbital floor fracture. Confidence: 95%.
3) Next best diagnostic step:
A full maxillofacial CT series with thin coronal and sagittal reconstructions should be obtained to assess the exact extent of fracture, possible muscle entrapment, and involvement of adjacent bony structures. Clinical correlation for diplopia, enophthalmos, or limitation of gaze is critical for management planning.
4) Key differential or confirmatory test:
Forced-duction testing can help confirm extraocular muscle entrapment. If visual disturbance or globe injury is suspected, ophthalmologic evaluation with slit-lamp and fundoscopic examination is necessary. MRI orbit can aid in evaluating soft-tissue entrapment if CT findings are equivocal.
5) Possible treatment or management:
** Mild, non-displaced fractures without muscle entrapment may be managed conservatively with oral antibiotics, avoidance of nose blowing, and close ophthalmologic follow-up. Surgical repair (via transconjunctival or subciliary approach) is indicated if there is persistent diplopia, muscle entrapment, enophthalmos >2 mm, or large defect on CT. Early reconstruction helps restore orbital volume and prevent long-term cosmetic deformity.
📑 Guidelines Summary (uploaded diagnosis) — Blowout fracture of orbit
Imaging of facial trauma after the primary survey guides detection of fractures, soft-tissue injury, and related craniofacial complications.
- Clinical variants include blunt midface trauma, mandibular injury, orbital trauma, or complex panfacial fractures.
- Noncontrast CT maxillofacial is first-line for suspected facial fractures once airway and hemodynamics are stable.
- Thin-section CT reformats in coronal and sagittal planes improve detection of subtle orbital floor or zygomatic fractures.
- MRI is indicated for optic nerve injury, ocular soft-tissue assessment, or vascular complication suspicion when CT is nondiagnostic.
- CT angiography is used for suspected arterial injury, pulsatile bleeding, or expanding hematoma to detect pseudoaneurysm or extravasation.
- Noncontrast head CT may accompany face CT to exclude intracranial injury if mechanism or neurologic findings warrant.
- Imaging is not indicated for isolated minor soft tissue trauma without deformity, malocclusion, or sensory deficit.
- Urgent imaging is needed for red flags such as orbital compartment syndrome, decreased vision, or unstable midface movement.
- Follow-up CT may be used post-reduction or for delayed complications like infection or nonunion.
- Pitfalls include motion artifact, inadequate z-axis coverage, and missing nondisplaced fractures in swollen tissues.
- In pediatric trauma, low-dose CT protocols and shielding should minimize radiation while preserving diagnostic detail.
🤖 Guidelines Summary (AI diagnosis) — Imaging of Facial Trauma Following Primary Survey
Guidelines Summary of AI Suggestion diagnosis is the same as the uploaded diagnosis. Please read above.
Comments
No comments yet.
Please log in to comment