Liver hyperattenuation from Amiodarone
Low confidence
High confidence
- Age: 54
- Sex: Female
- Modality: CT
- Region: Abdomen
- Country: N/A
- State: N/A
- City: N/A
- Diagnosis: Amiodarone Liver
🧠 AI Suggestion
1) Findings:
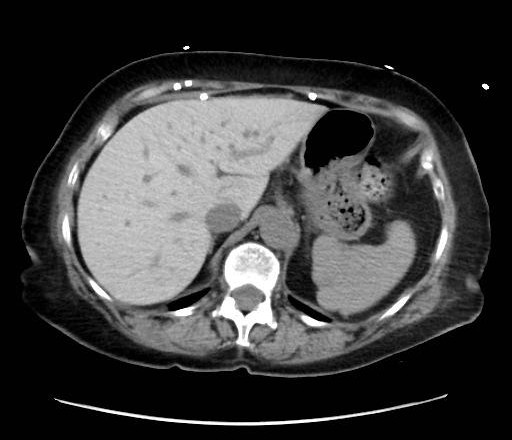
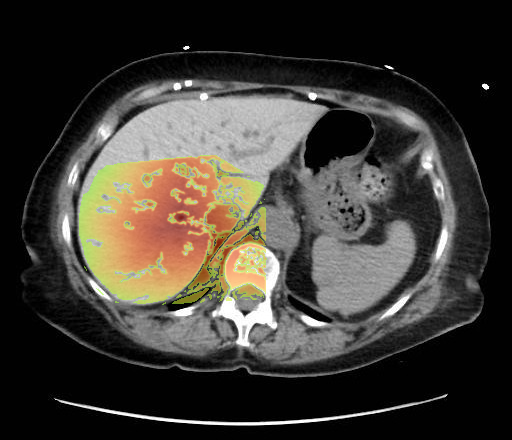
- Non-contrast axial CT through the upper abdomen.
- The liver (image-left, patient-right) demonstrates diffusely increased parenchymal attenuation relative to spleen (image-right, patient-left).
- Liver contour appears smooth, no focal mass identified at this level.
- Spleen (image-right, patient-left) of normal size and attenuation.
- Stomach fundus (image-right, patient-left) partially distended with air-fluid level.
- No ascites visible.
- No intrahepatic or extrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation.
- Osseous structures and visualized lung bases appear unremarkable at this slice.
2) Most likely diagnosis and why:
Diffuse hepatic parenchymal hyperattenuation due to amiodarone deposition (amiodarone liver). The liver is abnormally hyperdense on a non-contrast CT compared to the spleen, which is a classic imaging feature of amiodarone-induced hepatic iodine deposition. The attenuation difference eliminates common diffuse hypodensity causes such as steatosis, iron overload, or Wilson’s disease. Context consistency: Consistent. The uploader’s diagnosis of "Amiodarone Liver" directly matches the imaging appearance. Confidence: 90%.
3) Next best diagnostic step:
Correlate with clinical history of chronic amiodarone therapy. Consider obtaining liver function tests to evaluate hepatocellular injury or cholestasis. If there is diagnostic uncertainty, further imaging like MRI with T1/T2 relaxometry could help differentiate iron overload versus drug deposition.
4) Key differential or confirmatory test:
Differentials include hemochromatosis (iron overload) and Wilson’s disease (copper overload), both of which can cause abnormal hepatic attenuation. Confirmatory testing includes serum ferritin, transferrin saturation (for iron), or ceruloplasmin/copper studies (for Wilson’s). A liver biopsy can definitively confirm amiodarone deposition if clinically necessary.
5) Possible treatment or management:
The primary management is withdrawal or dose reduction of amiodarone if possible, depending on cardiac indications. Supportive monitoring with liver enzymes and imaging follow-up is indicated. If alternative antiarrhythmic therapy is feasible, drug discontinuation often improves liver changes. If progression to significant liver dysfunction occurs, hepatology consultation is warranted
- Non-contrast axial CT through the upper abdomen.
- The liver (image-left, patient-right) demonstrates diffusely increased parenchymal attenuation relative to spleen (image-right, patient-left).
- Liver contour appears smooth, no focal mass identified at this level.
- Spleen (image-right, patient-left) of normal size and attenuation.
- Stomach fundus (image-right, patient-left) partially distended with air-fluid level.
- No ascites visible.
- No intrahepatic or extrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation.
- Osseous structures and visualized lung bases appear unremarkable at this slice.
2) Most likely diagnosis and why:
Diffuse hepatic parenchymal hyperattenuation due to amiodarone deposition (amiodarone liver). The liver is abnormally hyperdense on a non-contrast CT compared to the spleen, which is a classic imaging feature of amiodarone-induced hepatic iodine deposition. The attenuation difference eliminates common diffuse hypodensity causes such as steatosis, iron overload, or Wilson’s disease. Context consistency: Consistent. The uploader’s diagnosis of "Amiodarone Liver" directly matches the imaging appearance. Confidence: 90%.
3) Next best diagnostic step:
Correlate with clinical history of chronic amiodarone therapy. Consider obtaining liver function tests to evaluate hepatocellular injury or cholestasis. If there is diagnostic uncertainty, further imaging like MRI with T1/T2 relaxometry could help differentiate iron overload versus drug deposition.
4) Key differential or confirmatory test:
Differentials include hemochromatosis (iron overload) and Wilson’s disease (copper overload), both of which can cause abnormal hepatic attenuation. Confirmatory testing includes serum ferritin, transferrin saturation (for iron), or ceruloplasmin/copper studies (for Wilson’s). A liver biopsy can definitively confirm amiodarone deposition if clinically necessary.
5) Possible treatment or management:
The primary management is withdrawal or dose reduction of amiodarone if possible, depending on cardiac indications. Supportive monitoring with liver enzymes and imaging follow-up is indicated. If alternative antiarrhythmic therapy is feasible, drug discontinuation often improves liver changes. If progression to significant liver dysfunction occurs, hepatology consultation is warranted
📑 Guidelines Summary (uploaded diagnosis) — Amiodarone Liver
Imaging selection for initial characterization of liver lesions depends on patient risk, clinical scenario, and lesion appearance on prior studies.
- Incidental lesion in low-risk adult: ultrasound or contrast-enhanced CT/MRI recommended for further evaluation.
- Known malignancy with suspected metastasis: multiphase contrast-enhanced CT or MRI preferred for staging and lesion characterization.
- Cirrhotic liver or chronic hepatitis: dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI with hepatobiliary agent offers highest diagnostic confidence for HCC.
- Homogeneous simple cyst on prior CT or ultrasound without risk factors: no further imaging needed.
- Lesion indeterminate on ultrasound: multiphase contrast-enhanced CT or MRI next step.
- Patient with renal insufficiency or contrast contraindication: non-contrast MRI sequences may help characterize lipid-rich lesions.
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasound is valuable when MRI or CT is not feasible or indeterminate.
- Do not use non-contrast CT alone for definitive lesion characterization due to limited specificity.
- Stable benign-appearing hemangioma or focal nodular hyperplasia requires no follow-up in low-risk patients.
- Growth, atypical enhancement, or indeterminate features warrant further imaging or biopsy referral.
- Avoid unnecessary repeat imaging of previously characterized benign entities to prevent overutilization.
🤖 Guidelines Summary (AI diagnosis) — Liver Lesion — Initial Characterization
Guidelines Summary of AI Suggestion diagnosis is the same as the uploaded diagnosis. Please read above.
Comments
No comments yet.
Please log in to comment