Mediastinal Teratoma
- Age: 9
- Sex: Female
- Modality: X-ray
- Region: Chest
- Country: N/A
- State: N/A
- City: N/A
- Diagnosis: Mediastinal Mature Teratoma
🧠 AI Suggestion
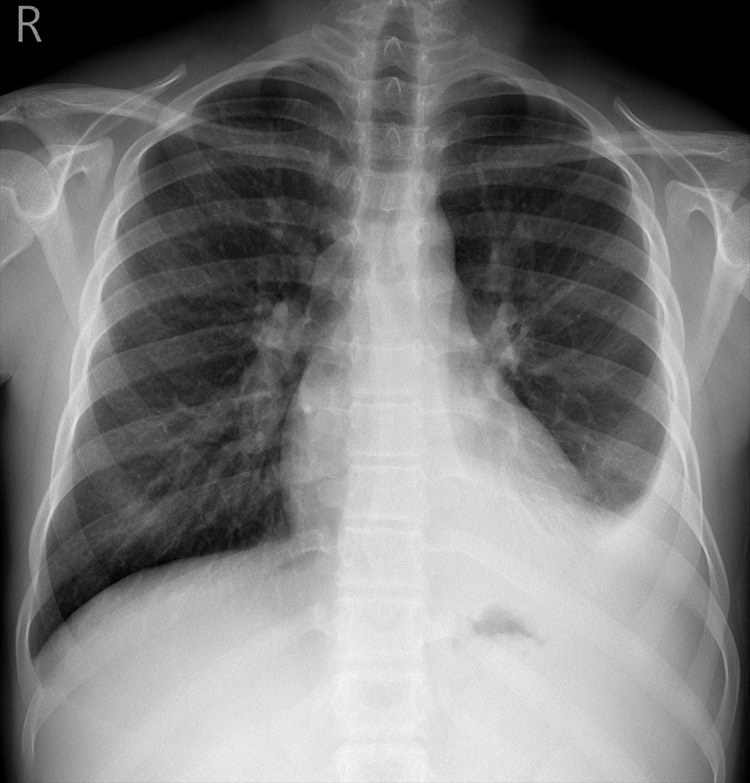
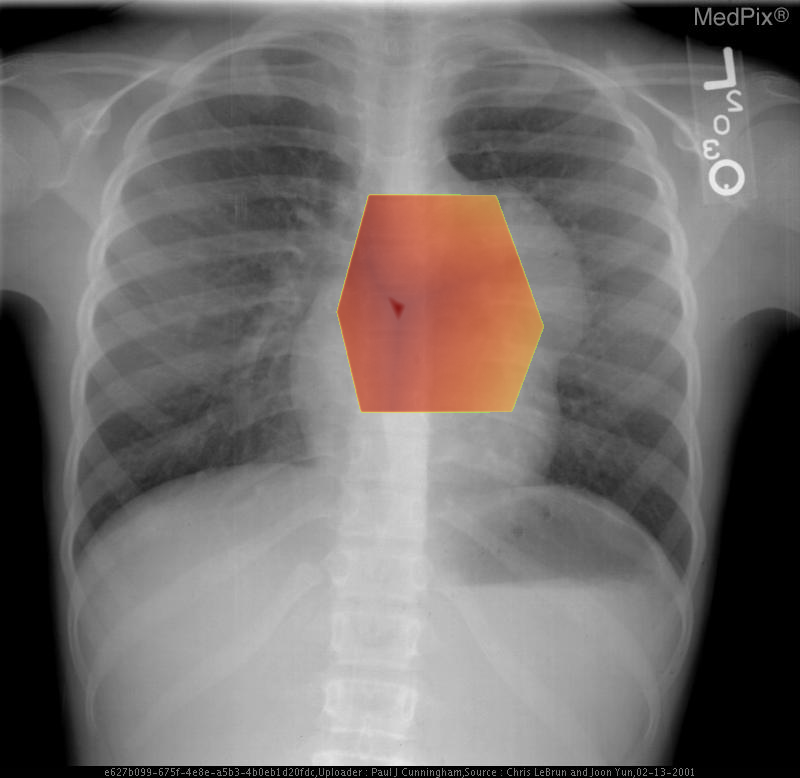
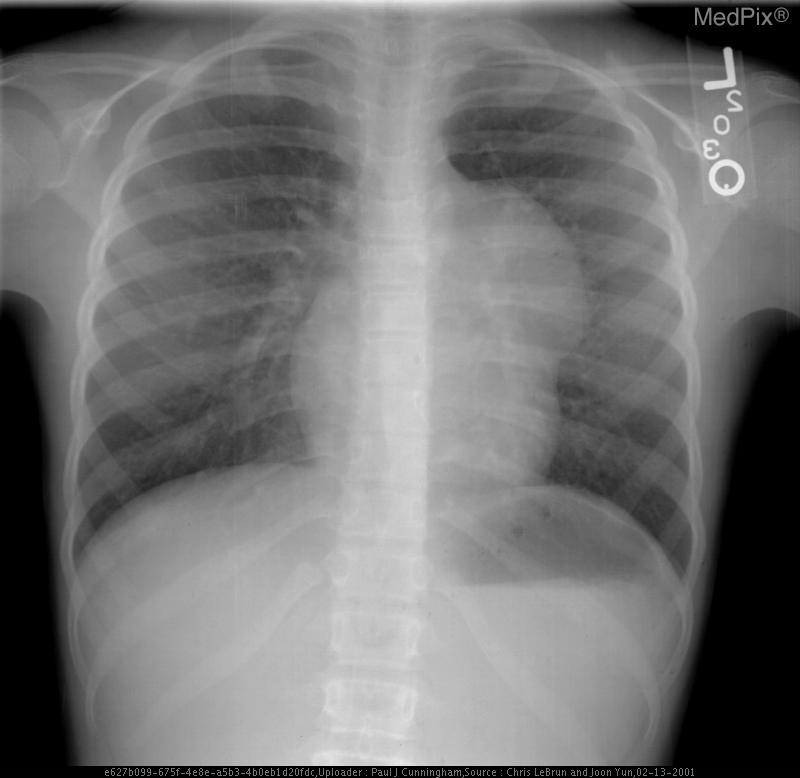
- Frontal chest radiograph, properly oriented: image-left = patient-right.
- Cardiac silhouette is mildly displaced toward the image-right (patient-left), suggesting mass effect from a mediastinal lesion.
- A well-circumscribed, rounded opacity occupies the image-left (patient-right) upper mediastinum, with smooth margins.
- The lesion shows heterogeneous internal density, including areas of relative lucency (suggesting fat) and opacity (possibly soft tissue or calcification).
- Lungs otherwise clear without focal consolidation or effusion.
- Bony thorax intact with no visible rib destruction or vertebral abnormality.
- Trachea slightly deviated toward image-right (patient-left), consistent with mild mediastinal shift.
- Diaphragms symmetric; cardiopericardial silhouette otherwise unremarkable except for mass effect.
2) Most likely diagnosis and why:
Anterior mediastinal teratoma. The well-defined, heterogeneous mass in the anterior mediastinum with soft tissue and possible fatty or calcific elements is characteristic of a mediastinal teratoma. Leftward (patient-left) cardiac displacement and tracheal shift support a space-occupying lesion in the anterior mediastinum. Context consistency: Consistent. The reported age (child) and sex (female) align with a known demographic pattern for benign mediastinal teratoma. Confidence: 90%.
3) Next best diagnostic step:
A contrast-enhanced chest CT should be performed to delineate the lesion’s exact composition (fat, soft tissue, calcium, cystic elements) and its relationship to surrounding structures such as great vessels and pericardium. MRI may be helpful if further soft-tissue characterization is needed or if cystic-versus-solid proportions are unclear.
4) Key differential or confirmatory test:
Main differentials include thymic lesion (thymoma/thymolipoma), lymphoma, or bronchogenic cyst. CT attenuation and presence of fat or calcification are helpful distinguishing features for teratoma. If uncertainty persists after imaging, surgical excision or image-guided biopsy provides definitive histologic confirmation, though biopsy is often avoided if imaging is classic.
5) Possible treatment or management:
** Surgical excision (typically via median sternotomy or thoracotomy) is the treatment of choice to prevent rupture, infection, or compressive symptoms. Most mature teratomas are benign, and prognosis is excellent after removal. Postoperative follow-up includes histopathologic confirmation and surveillance imaging for recurrence.
📑 Guidelines Summary (uploaded diagnosis) — Mediastinal Mature Teratoma
Imaging of pediatric soft tissue vascular anomalies guides classification, treatment planning, and detection of complications in vascular malformations and infantile tumors.
- Initial evaluation relies on clinical findings; image only if diagnosis uncertain, deep lesion, or complication suspected.
- Ultrasound with Doppler is the first-line study for lesion flow characterization and extent assessment.
- MRI with contrast precisely defines anatomic extent and tissue involvement when intervention or surgery is planned.
- Non-contrast MRI sequences demonstrate subcomponents, hemorrhage, or fat; dynamic contrast bolus sequences separate high- and low-flow lesions.
- CT or CT angiography is reserved for bone involvement or when MRI is contraindicated or unavailable.
- MR or CT venography is useful for extensive venous malformations or thrombosis assessment.
- Do not image purely superficial hemangiomas unless atypical features or lack of involution by 12 months are present.
- Repeat imaging indicated for progressive pain, growth, ulceration, or prior to sclerotherapy or embolization.
- Acute bleeding, high-output cardiac failure, or consumptive coagulopathy are red flags needing prompt cross-sectional imaging.
- Post-treatment follow-up uses the same modality as baseline to evaluate residual lesion and therapy response.
- Pitfalls include misclassifying rapidly involuting congenital hemangiomas as vascular malformations and mistaking flow artifacts for rapid shunting.
- Soft Tissue Vascular Anomalies: Vascular Malformations and Infantile Vascular Tumors (Non-CNS)-Child
🤖 Guidelines Summary (AI diagnosis) — Imaging of Mediastinal Masses
Imaging of mediastinal masses focuses on identifying lesion compartment, characterization, and assessment for invasion or malignancy across clinical scenarios.
- Initial evaluation of incidental mediastinal widening on chest radiograph warrants chest CT with IV contrast.
- Noncontrast CT may be used if contrast contraindicated but limits vascular and soft-tissue differentiation.
- MRI adds value for cystic lesions, vascular involvement, and differentiating thymic hyperplasia from neoplasm.
- Acute presentation with compressive symptoms or suspected hemorrhage requires contrast-enhanced CT urgently.
- For suspected vascular or venolymphatic malformation, CT angiography or MR angiography improves delineation.
- PET/CT aids staging of suspected malignant mediastinal masses or lymphoma after initial CT or MRI.
- If lesion is clearly benign (e.g., typical pericardial cyst), further imaging follow-up may be unnecessary.
- Routine follow-up CT can assess interval change for indeterminate lesions managed conservatively.
- Avoid repeated CTs in stable benign lesions or postoperative scar without new clinical concern.
- Misregistration and motion artifacts are pitfalls—use multiplanar review to confirm margins and invasion.
Comments
No comments yet.
Please log in to comment